Visit Continental Tires in your country for local vehicle fitment
# CO₂ Emissions & VECTO
Change is coming. We're ready, are you?
All about CO₂ Emissions regulations & VECTO
It's the year of action.
To keep our world moving, we all have to take action and invest in change today. Not only to benefit from staying competitive in the future, but above all to live on a healthier planet. That's why bringing down fuel consumption and thus CO₂ emissions is key. To combat climate change in line with the Paris Agreement, the first carbon dioxide emissions regulations for new heavy-duty vehicles (HDV) have been introduced. These will mean cutting average CO₂ emissions from new heavy-duty vehicles by 15% by 2025 and by 30% by 2030 compared to 2019/2020. To ensure the reduction targets are met, the European Commission has introduced a simulation tool called VECTO — short for Vehicle Energy Consumption Calculation Tool.
All about CO₂ emissions regulations & VECTO
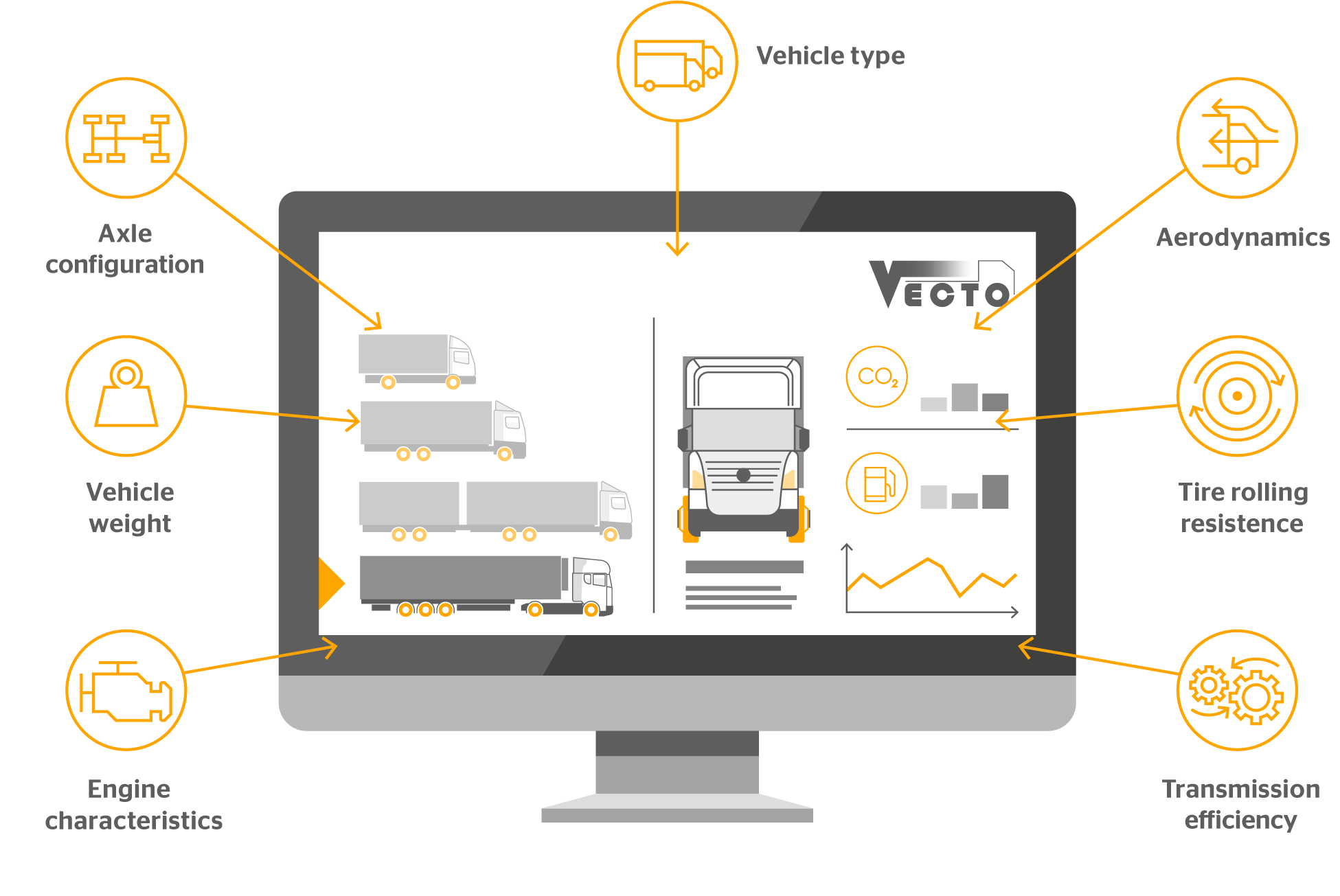
Who is affected by the regulations? How will the new CO₂ emissions regulations make road transportation more efficient? What is VECTO? How will it provide greater transparency on your fleet expenditures? And what are the main contributors to fuel consumption and CO₂ emissions? Read the infographic to find out.
Learn more about the CO₂ emissions regulations, VECTO and why these things are so important.
Europe's first carbon dioxide (CO₂) regulations for heavy-duty vehicles (HDV) has a very simple objective: radically reducing CO₂ emissions from trucks, buses and coaches. To ensure these reduction targets are met, the European Commission has introduced a computer-assisted simulation tool called VECTO - short for Vehicle Energy Consumption Calculation Tool. With VECTO, vehicle manufacturers can simulate the fuel consumption and thus the carbon dioxide emissions of different heavy-duty vehicle configurations.

How is your transport business going to be affected?
The new regulations set out to reduce carbon dioxide (CO2) emissions. To achieve this, truck manufacturers need to invest in the development of technology that makes their vehicles more fuel efficient, because fuel consumption is directly linked to emissions. This will not only result in your fleet using less fuel in the future; it will also provide greater transparency when it comes to individual vehicle configurations.

Which vehicle configurations are affected?
The regulations apply to a huge range of trucks — from two axles upwards and either rigid or articulated. Vehicles like these contribute 70% of the total CO₂ emissions from heavy-duty vehicles. The regulations are continuously being reviewed and extended to additional truck, trailer, bus and coach configurations and vehicle groups. Further regulations took effect in January 2020.
Did you know?
The level of CO₂ emissions is directly related to fuel consumption. The three main factors impacting on fuel consumption and emissions are the vehicle's engine, the aerodynamic drag and the rolling resistance of the tires.

3 main factors impacting on fuel consumption and CO₂ emissions: engine, aerodynamics and the rolling resistance of tires.